This comprehensive guide examines emerging e-commerce security threats in 2025, including new cyber risks, data breaches, and fraud tactics, with expert insights to protect your online store
The e-commerce security landscape in 2025 has become increasingly dangerous as cybercriminals deploy sophisticated AI-powered attacks and exploit emerging vulnerabilities. It is dominated by increasingly advanced cyber threats, sophisticated payment fraud, to large-scale data breaches and targeted phishing designed to compromise customer accounts.
As online shopping continues to grow, so do the vulnerabilities within ecommerce platforms, APIs, third-party apps, and digital payment systems. Online retailers must strengthen online store security, protect customer data, and reduce exposure to emerging cybersecurity risks that can damage revenue and reputation. This complete analysis highlights the most critical ecommerce threats of 2025 and provides actionable strategies to help businesses stay secure in an evolving digital environment.
According to DeepStrike’s 2025 analysis:
“global cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually, with sophisticated threats evolving at record pace.”
E-commerce businesses face unique challenges as they handle sensitive payment data and customer information that criminals actively target.

Source:Cybersecurity Statistics 2025
The 2025 E-commerce Threat Landscape
The threat landscape facing e-commerce businesses in 2025 is characterized by increased sophistication, volume, and diversity of attacks.
SentinelOne’s cybersecurity trends report reveals that:
“More than 30,000 vulnerabilities were disclosed last year, a 17 percent increase from previous figures, reflecting the steady rise in cyber risks.”
Key Trends Shaping 2025 Threats
AI-Powered Attack Evolution: Criminals now use artificial intelligence to create more convincing phishing campaigns, automate vulnerability discovery, and evade traditional security defenses. AI enables attackers to operate at unprecedented scale and sophistication.
Third-Party Supply Chain Attacks: According to RSI Security’s 2025 trends analysis:
“Third-party risk is now one of the top attack vectors in ecommerce.”
Criminals compromise vendors, plugins, and service providers to access multiple e-commerce targets through single exploits.
Mobile Commerce Targeting: As mobile shopping grows, attackers increasingly focus on mobile applications, mobile payment systems, and vulnerabilities specific to mobile platforms.
Regulatory Complexity: New compliance requirements like PCI DSS 4.0.1 create additional security challenges as businesses struggle to meet expanding regulatory demands while maintaining operations.
Top E-commerce Security Threats in 2025
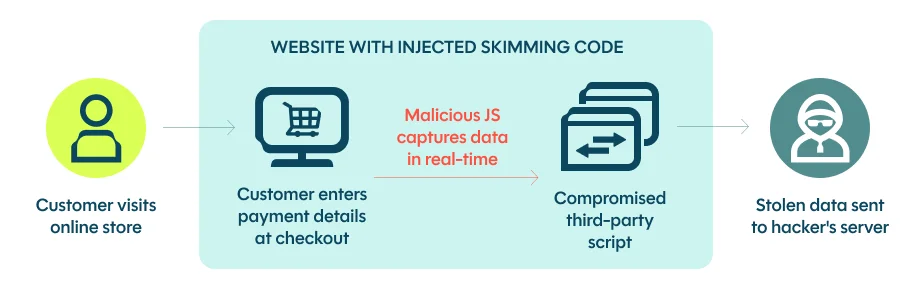
1. Magecart Attacks: Digital Card Skimming
Magecart attacks represent one of the most dangerous e-commerce threats in 2025. Trustwave’s Magecart analysis documents that:
“CosmicSting impacted 75% of Adobe Commerce and Magento platforms, compromising thousands of e-commerce websites in one of 2024’s most widespread attacks.”
How Magecart Works: Attackers inject malicious JavaScript code into e-commerce checkout pages. According to Imperva’s Magecart explanation:
“This code captures credit card information, CVV codes, and personal details as customers enter them, sending data to criminal servers before processing legitimate transactions.”
Source Defense reports that:
“Magecart infections skyrocketed by 103% in just six months, demonstrating explosive growth in these attacks.”
Why Magecart is Dangerous: The attacks are difficult to detect because they operate client-side in customer browsers rather than on merchant servers. Traditional security tools don’t see the theft happening, and customers don’t realize their payment information has been stolen until fraudulent charges appear.
Mitigation Priorities: Implement client-side security monitoring, use Content Security Policies (CSP), regularly audit third-party scripts, deploy web application firewalls, and conduct frequent security scans specifically for Magecart indicators.
Source: DataDome – Prevent Magecart Attacks 2025
2. Advanced Phishing and Spear-Phishing
Mageplaza’s threat analysis identifies that:
“Phishing attacks ranked first among the top 10 e-commerce security threats in 2025, having evolved beyond generic spam emails to become more personalized and deceptive.”
Spear-Phishing Targeting: Criminals research e-commerce employees on LinkedIn and social media to craft highly targeted phishing messages. Finance departments receive fake invoices from compromised vendor accounts, while IT staff see urgent security alerts from fake service providers.
AI-Enhanced Phishing: Artificial intelligence now generates convincing phishing emails at scale, personalizes messages based on scraped data, creates deepfake voice and video for vishing attacks, and adapts tactics in real-time based on victim responses.
Impact on E-commerce: Successful phishing provides criminals with administrative credentials to access e-commerce platforms, payment systems, and customer databases. Business email compromise stemming from phishing causes billions in losses annually.
Mitigation Priorities: Conduct regular security awareness training with phishing simulations, implement multi-factor authentication on all accounts, deploy advanced email filtering with AI detection, verify requests through secondary channels, and establish clear verification procedures for financial transactions.
3. Ransomware Targeting E-commerce Operations
Ransomware attacks have evolved to specifically target e-commerce businesses because downtime directly equals revenue loss, creating pressure to pay ransoms quickly. Cloud Security Alliance notes that:
“Sophisticated ransomware represents a top emerging threat requiring proactive and adaptive security measures.”
Double Extortion Tactics: Modern ransomware not only encrypts e-commerce databases and systems but also steals customer data before encryption. Criminals threaten to publish stolen payment information and personal data if ransoms aren’t paid, even if businesses can restore from backups.
Supply Chain Ransomware: Attackers increasingly target e-commerce vendors, shipping partners, and payment processors, knowing that disrupting these services impacts multiple online stores simultaneously.
Mitigation Priorities: Implement immutable backup systems following 3-2-1-1 rules, segment networks to contain infections, maintain offline recovery systems, deploy endpoint detection and response solutions, and develop tested incident response procedures.
4. Account Takeover (ATO) Attacks
Account takeover attacks compromise customer accounts through stolen credentials obtained from data breaches, phishing, or credential stuffing. Shopify’s retail cybersecurity guide explains that:
“Criminals use stolen credentials to hack into customer accounts, make unauthorized purchases, or steal personal information.”
Credential Stuffing: Criminals test millions of username-password combinations stolen from other breaches against e-commerce sites. Since many customers reuse passwords, this succeeds at alarming rates.
Impact: Once inside accounts, criminals make fraudulent purchases using stored payment methods, steal loyalty points and gift cards, access personal information for identity theft, and gather data for further targeted attacks.
Mitigation Priorities: Require multi-factor authentication for customer accounts, implement bot detection and CAPTCHA, monitor for credential stuffing patterns, enforce password complexity requirements, alert customers to suspicious login activity, and provide breach notification services.
5. DDoS Attacks Disrupting Operations
Distributed Denial of Service attacks overwhelm e-commerce websites with traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate customers. Astra Security’s threat overview identifies:
“DDoS is a major concern, causing unprotected services to fail.”
Evolving DDoS Tactics: Modern DDoS attacks target application layers rather than just network infrastructure, requiring fewer resources while being harder to mitigate. Some use IoT botnets comprising millions of compromised devices.
Extortion Component: Criminals often demand ransom to stop DDoS attacks, threatening continued downtime if payments aren’t made. Even businesses with DDoS protection face difficult decisions about paying extortion.
Financial Impact: Every minute of downtime costs e-commerce businesses thousands in lost sales. Peak shopping periods like holidays see increased DDoS attacks knowing merchants face maximum pressure to restore operations quickly.
Mitigation Priorities: Deploy cloud-based DDoS protection services, implement traffic filtering and rate limiting, maintain redundant infrastructure, establish incident response procedures for rapid mitigation, and never negotiate with extortionists.
6. SQL Injection Exploiting Database Vulnerabilities
SQL injection remains prevalent because many e-commerce platforms use outdated code or insufficiently validated user inputs. Attackers insert malicious SQL commands through search boxes, product filters, or URL parameters to manipulate database queries.
What Attackers Steal: SQL injection enables criminals to extract entire customer databases including payment information, download order histories and business intelligence, modify product prices or inventory levels, delete critical business data, and gain administrative access to e-commerce platforms.
Mitigation Priorities: Use parameterized queries and prepared statements, implement input validation and sanitization, deploy web application firewalls, conduct regular vulnerability scanning, keep platforms and plugins updated, and follow secure coding practices.
Source: E-commerce Security Threats 2025
7. Third-Party and Supply Chain Compromises
RSI Security emphasizes that:
“Third-party risk is now one of the top attack vectors in ecommerce.”
E-commerce businesses integrate numerous plugins, payment processors, analytics tools, and service providers each representing potential security vulnerabilities.
Why Third-Party Attacks Succeed: Criminals compromise a single popular plugin or service that thousands of e-commerce stores use, instantly gaining access to multiple targets through one exploit. The SolarWinds and other major supply chain attacks demonstrate this approach’s effectiveness.
Recent Examples: The CosmicSting vulnerability affecting 75% of Adobe Commerce and Magento platforms showed how single vulnerabilities in popular platforms can compromise thousands of online stores simultaneously.
Mitigation Priorities: Conduct vendor security assessments before integration, monitor third-party services for security updates, implement least-privilege access for external services, maintain inventories of all integrated services, establish contractual security requirements with vendors, and have contingency plans for vendor breaches.
8. AI-Powered Fraud and Bot Attacks
Artificial intelligence has transformed e-commerce fraud, enabling criminals to operate at scales and sophistication levels previously impossible. Help Net Security’s fraud trends analysis highlights:
“how fraud trends in 2025 highlight growing risks in eCommerce.”
AI-Driven Threats Include:
- Automated account creation and credential stuffing
- Smart bots that mimic human behavior to evade detection
- AI-generated fake reviews and ratings manipulation
- Intelligent price scraping and competitive intelligence theft
- Automated vulnerability discovery and exploitation
- Scalper bots purchasing limited inventory for resale
Mitigation Priorities: Deploy AI-powered fraud detection systems, implement behavioral analysis and anomaly detection, use advanced CAPTCHA and bot detection, monitor for unusual purchasing patterns, establish rate limiting and velocity checks, and continuously update bot mitigation strategies as attacks evolve.
9. Mobile Commerce Vulnerabilities
Mobile shopping growth has created new attack surfaces as criminals exploit mobile-specific vulnerabilities. Mobile applications often have weaker security than websites, mobile users are more susceptible to phishing on smaller screens, and public Wi-Fi creates man-in-the-middle attack opportunities.
Mobile-Specific Threats: Malicious apps mimicking legitimate stores, SMS phishing (smishing) with fake delivery notifications, insecure mobile payment implementations, session hijacking on mobile devices, and malware targeting mobile banking applications.
Mitigation Priorities: Implement certificate pinning in mobile apps, use secure coding practices for mobile development, conduct mobile-specific penetration testing, educate customers about mobile security risks, require biometric authentication, and monitor app stores for fake versions of your application.
10. Payment Fraud and Chargeback Abuse
Payment fraud continues evolving with criminals using stolen card data, synthetic identities, and chargeback abuse to defraud e-commerce merchants. Binmile’s security analysis notes that:
“2025 threats have shown an increase in proximity-based and infrastructure-oriented attack methods.”
Chargeback Fraud: Customers receive products or services but dispute charges with banks, claiming they never authorized purchases or received items. While sometimes legitimate, organized chargeback fraud costs merchants significantly.
Mitigation Priorities: Implement strong authentication including 3D Secure, use address verification systems (AVS) and CVV validation, deploy AI-powered fraud detection analyzing purchasing patterns, maintain detailed transaction records and proof of delivery, establish clear refund and return policies, and respond promptly to chargeback claims with evidence.
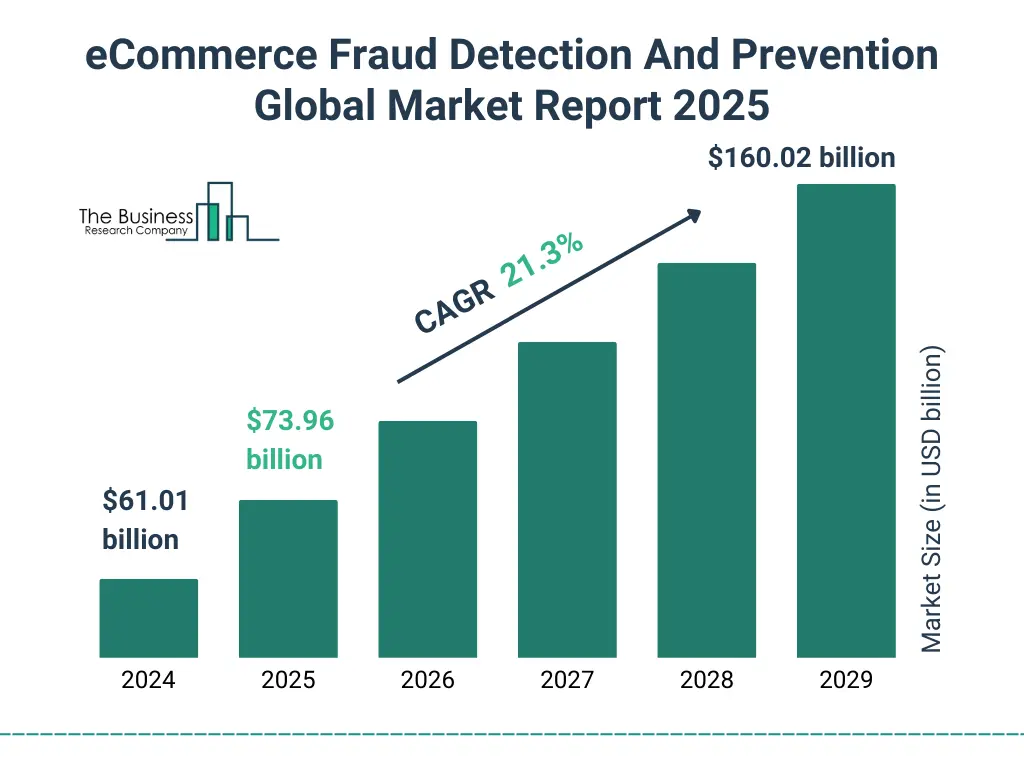
Source: Fraud Trends 2025
Industry Statistics: The Scale of E-commerce Threats
Understanding the numbers helps prioritize security investments:
Vulnerability Growth: SentinelOne reports:
“More than 30,000 vulnerabilities were disclosed last year, a 17% increase, indicating expanding attack surfaces.”
Magecart Surge: Source Defense documented a:
“103% increase in Magecart infections in just six months, showing explosive growth in digital skimming.”
Platform Compromise: The CosmicSting attack impacted 75% of Adobe Commerce and Magento platforms, demonstrating how a single vulnerability can affect thousands of stores.
Financial Impact: Global cybercrime costs reach $10.5 trillion annually, with e-commerce representing a significant portion due to valuable payment data and customer information.
Phishing Prevalence: Phishing ranked first among the top 10 e-commerce security threats, showing social engineering remains the most effective attack vector.
Mitigation Priorities for 2025
E-commerce businesses should prioritize these security measures:
Immediate Priorities
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Require MFA for all administrative accounts, customer accounts handling payment methods, and access to sensitive business systems.
Deploy Web Application Firewalls: Use WAFs specifically configured for e-commerce threats including SQL injection, XSS, and Magecart detection.
Establish Security Monitoring: Implement 24/7 monitoring for suspicious activity, failed login attempts, unusual transactions, and security incidents.
Update Everything: Keep platforms, plugins, and all software current with latest security patches. Subscribe to security bulletins for technologies you use.
Conduct Employee Training: Regular security awareness training focusing on phishing recognition, social engineering tactics, and secure business practices.
Medium-Term Priorities
Implement Client-Side Security: Deploy tools specifically monitoring JavaScript execution on payment pages to detect Magecart and similar attacks.
Enhance Fraud Detection: Use AI-powered fraud detection analyzing purchasing patterns, device fingerprinting, and behavioral analytics.
Strengthen Third-Party Security: Assess vendor security, establish contractual security requirements, and continuously monitor integrated services.
Develop Incident Response: Create tested procedures for responding to breaches, ransomware, DDoS attacks, and other incidents.
Regular Security Assessments: Conduct quarterly vulnerability scans, annual penetration testing, and continuous security audits.
Long-Term Priorities
Build Security Culture: Make security everyone’s responsibility through ongoing training, clear policies, and leadership commitment.
Adopt Zero Trust Architecture: Implement verification for every access request, eliminate trust assumptions, and segment networks.
Invest in Advanced Technologies: Consider AI-powered security tools, behavioral analytics, and next-generation security platforms.
Maintain Compliance: Stay current with PCI DSS, GDPR, and other regulatory requirements as they evolve.
Plan for Incidents: Develop comprehensive business continuity and disaster recovery plans tested through regular exercises.
Conclusion
The e-commerce threat landscape in 2025 is more dangerous than ever, with AI-powered attacks, sophisticated Magecart campaigns, third-party compromises, and emerging mobile threats creating unprecedented challenges for online merchants. The 103% surge in Magecart infections, 75% platform compromise rates, and $10.5 trillion global cybercrime costs demonstrate the severity and scale of threats facing e-commerce businesses.
However, e-commerce merchants can protect themselves through comprehensive security strategies addressing the top threats identified in this analysis. Prioritizing multi-factor authentication, web application firewalls, security monitoring, regular updates, employee training, client-side security, fraud detection, third-party management, incident response, and regular assessments creates layered defenses that significantly reduce risk.
The key to e-commerce security in 2025 is understanding that threats continuously evolve, requiring adaptive, proactive approaches rather than reactive responses. Merchants must invest in security as a fundamental business requirement rather than an optional expense, recognizing that customer trust and business survival depend on effective threat mitigation.
By implementing the mitigation priorities outlined in this guide and staying informed about emerging threats, e-commerce businesses can navigate the challenging 2025 threat landscape while protecting customers, maintaining operations, and building competitive advantages through superior security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most significant e-commerce security threats emerging in 2025?
The leading threats in 2025 include AI-powered phishing attacks, automated credential-stuffing using large botnets, supply-chain compromises in third-party integrations, deepfake-enabled fraud, and increasingly sophisticated API exploitation targeting checkout systems
How are AI-driven attacks changing the e-commerce security landscape?
Why are APIs becoming a major vulnerability for online retailers?
As e-commerce platforms rely heavily on APIs for payments, inventory sync, and logistics, attackers are focusing on API endpoints to extract data, manipulate order flows, or execute unauthorized transactions. Poor access controls and weak authentication amplify this risk.
What steps can businesses take to mitigate 2025’s new e-commerce threats?
Companies should adopt zero-trust access models, deploy AI-enhanced fraud detection, enforce strong API authentication, conduct frequent penetration testing, and monitor third-party integrations for abnormal behavior or update delays.
How can retailers protect customers from increasing identity and payment fraud?
Key measures include multi-factor authentication, real-time transaction monitoring, tokenization of payment data, device fingerprinting, and continuous verification of account activity using behavioral analytics.
